خوب مقاله ی قبلی که رو که ترجمه کردم زیاد راضی نشدم چون هنوز خیلی سوال توی ذهنم بود که دقیقا این ها دارن چی کار میکنن و …
برای همین دو سه تا سایت دیگه رو هم بررسی کردم تا موضوع یکم بیشتر روشن بشه :
مقاله اول : از آقای Oleg Tsibulevskiy
IEnumerable and IEnumerator interfaces, thanks to them we can iterate over the elements in a loop, let’s go look how.
میگه که هر دوتای IEnumerable and IEnumerator هایی هستند که با استفاده ازشون میتونی توی المان ها پیمایش کنیم ، دستشون درد نکنه.
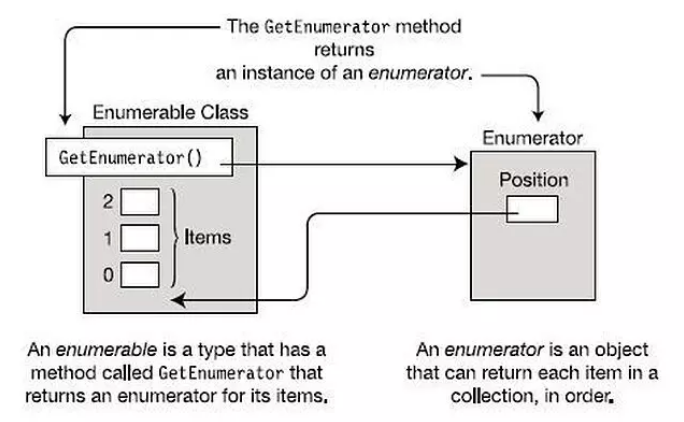
Element
We will use the Restaurant class as elements in the examples:
المان که میخوایم بررسی کنیم فکر کنید کلاس رستورانه
class Restaurant { string Name { get; set; }
bool IsOpened { get; set; }
public Restaurant(string name, bool isOpened) {
Name = name; IsOpened = isOpened; } }IEnumerable
The IEnumerable interface defines only one method GetEnumerator()which returns an enumerator that iterates through a collection through implementing the interface IEnumerator. IEnumerator we will review it later, for now, let’s look at the implementation of the IEnumerable interface.
All that we need for this is to create a class that will store a list of elements and implement IEnumerable, create an instance, and iterate over it in a foreach loop.
میگه که اینترفیس IEnumerable یه متد میخواد (یا یه متد رو تعریف کرده) به اسم GetEnumerator رو که یک enumerator رو که رو کالشکن ها پیمایش میکنه رو به ما برمیگردونه(البته این رو در نظر بگیرید که خوده این هم باید یه اینترفیس دیگه به اسم IEnumerator رو درست کنه)
class Restaurants : IEnumerable
{
readonly public List<Restaurant> restaurants = new List<Restaurant>
{
new Restaurant("Pizza", true),
new Restaurant("Hamburger", false),
new Restaurant("Bread", true)
};
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator() => restaurants.GetEnumerator();
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Restaurants restaurants = new Restaurants();
foreach (Restaurant restaurant in restaurants)
{
Console.WriteLine(restaurant.Name);
}
//Output:
//Pizza
//Hamburger
//Bread
}
}As shown, we created a class Restaurants which implements IEnumerable. For simplicity, we created a list of restaurants inside the class and we’re using the non-generic types, but you can pass the list to the constructor and use generic version of interface IEnumerable T. The method GetEnumerator() returns the built-in enumerator from the restaurants list, we can do this because List implements the IEnumerable as well. To test our code we created an instance of Restaurants object and run a foreach loop.
خوب همونطور که معلومه ما اومدیم کلاس رستوران رو با استفاده از IEnumerable پیاده سازی کردیم. خوب برای ساده سازی اومدیم توی کلاس رستوران یه لیست درست کردیم با تایپ Nongeneric ولی خوب میتونیم لیست رو بفرستیم توی constructor و از اینترفیس generic IEnumerable استفاده کنیم.
متد GetEnumerator میاد و enumerator لیست رستوران ها رو به ما میده، چطور؟ چون list هم اینترفیس IEnumerable رو اوکی کرده.
All this is cool, but what if we don’t want to use the default implementation of the IEnumerator interface and we need to add some of our own logic? For this, we need to review the IEnumerator interface.
حالا اگر ما پیاده سازی default اینترفیس IEnumerator رو نخوایم چی ؟ و بخوایم یه منطقی رو هم خودمون بهش اضافه کنیم توی این کار :
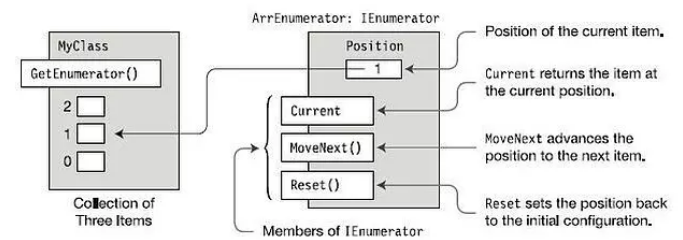
IEnumerator
IEnumerator is an interface which lets you get the Current element from a collection. It has two methods:
1. MoveNext - Advances the enumerator to the next element of the collection. It returns true if the enumerator was successfully set to the next element and false if the enumerator has reached the end of the collection.
2. Reset - Sets the enumerator to its initial position, which is before the first element in the collection.
خوب حالا اینترفیس IEnumerator چیه؟ این اینترفیس بهتون اجازه میده که المان جاری ( Current ) یک کالکشن رو بگیرید که خودش باز هم دو تا متد داره :
متد MoveNext که enumerator المان هاشو رو توی یک کالکشن یکی یکی میبره جلو . خروجی این متد true و false هستش. اگر المان بعدی باشه و enumerator بره المان بعد که true در غیر این صورت false رو برمیگردونه .
متد reset که enumerator رو ریست میکنه و میبره از سره اولین المان کالکشن شروع میکنه.
namespace System.Collections{
public interface IEnumerator {
object? Current { get; }
bool MoveNext();
void Reset(); }}Knowing this, we can now create a custom enumerator. For example, we want to iterate over only opened restaurants and IEnumerator can help us with this. First, we need to create a class that will get a list of elements and implement interface IEnumerator.
خوب حالا دونستن این قضیه بهمون کمک میکنه که بیایم یه enumerator مدل خودمون رو درست کنیم. مثلا ما فقط میخوایم فقط اون رستوران هایی که باز هستند رو IEnumerator بهمون بده.
class OpenRestaurantsEnumerator : IEnumerator
{
private readonly List<Restaurant> _restaurants;
private int _position = -1;
public OpenRestaurantsEnumerator(List<Restaurant> restaurants)
{
_restaurants = restaurants;
}
public object Current
{
get
{
if (_position == -1 || _position >= _restaurants.Count)
throw new InvalidOperationException();
return _restaurants[_position];
}
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
while(_position < _restaurants.Count)
{
_position++;
if (_position < _restaurants.Count && _restaurants[_position].IsOpened)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void Reset()
{
_position = -1;
}
}The class contains the properties _restaurants and _position.
_position - Needed for storing the current position
_restaurants - Needed for storing the list of restaurants
خوب اومدیم یه کلاس ساختیم با پراپرتی های restaurants و position
The positions start from -1 because the first method that will be called isMoveNext(), which moves the position forward by one. Only then can we access the Current property to get the element at the current position.
The MoveNext() method will increase the position pointer and check if the next restaurant is open until it gets to the end of the list.
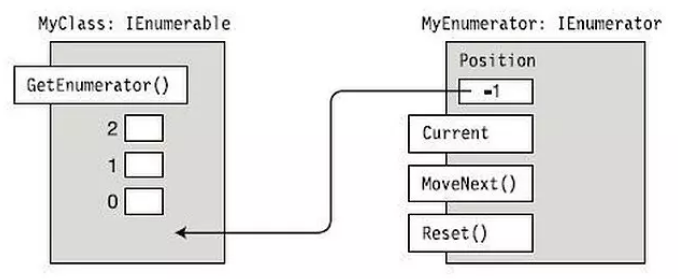
خوب position از -1 شروع میشه (؟) چون که اولین متد ای که باید صدا بشه isMoveNext که خودش یه یه خونه میبره جلو موقعیت یا جایگاه رو و بعد از این اتفاق ما میتونیم به پراپرتی جاری دسترسی پیدا کنیم و المان رو با جایگاهش بگیریم . متد MoveNext هم میاد pointer جایگاه رو یکی افزایش میده و میاد چک میکنه که رستوران بازه یا بسته.
Now we need to create and return an instance of our enumerator from the class implemented IEnumerable interface GetEnumerator() method.
حالا باید بیایم یه نمونه از enumerator از کلاس بگیریم.
اون کلاس باید اینترفیس IEnumerable و متد GetEnumerator رو داشته باشه (پیاده سازی کرده باشه)
class Restaurants : IEnumerable
{
readonly public List<Restaurant> restaurants = new List<Restaurant>
{
new Restaurant("Pizza", true),
new Restaurant("Hamburger", false),
new Restaurant("Bread", true)
};
public GetEnumerator() => new OpenRestaurantsEnumerator(restaurants);
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Restaurants restaurants = new Restaurants();
foreach (Restaurant restaurant in restaurants)
{
Console.WriteLine(restaurant.Name);
}
//Output:
//Pizza
//Bread
}
}Conclusion
Sure, it looks like a lot of code to iterate over restaurants, but your logic could be more complicated and you might want to hide that behind a class. In that case, implementing a custom IEnumerable and IEnumerator can be a great solution
خوب در نهایت نتیجه :
اگر بخوایم یه لاجیک و یه منطقی رو برای پایش در یک کالکشن داشته باشیم یکی از بهترین راه هاش استفاده از IEnumerable and IEnumerator هستش.